Adsorption behavior and mechanism of CO2 in Longmaxi shale gas reservoir
ID:291
Submission ID:347 View Protection:PUBLIC
Updated Time:2022-05-21 14:29:46
Hits:1288
Poster Presentation
Start Time:2022-05-27 18:06 (Asia/Shanghai)
Duration:1min
Session:[ps] Poster Seesion » [ps] Poster Session
Abstract
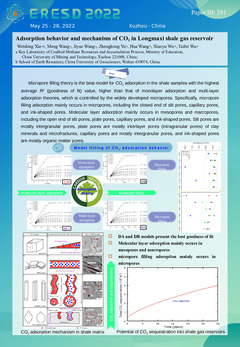
Shale gas reservoir is a potential sequestration space of excess CO2 in the atmosphere. This work clarified CO2 adsorption behavior in Longmaxi shale, and Langmuir, BET (Brunauer-Emmett-Teller), DA (Dubinin-Astakhov), and DR (Dubinin-Radushkevitvh) models presented highly applicable on the fitting process of CO2 adsorption experimental data. Micropore filling theory was the best model for CO2 adsorption in the shale samples with the highest average R2 (goodness of fit) value, higher than that of monolayer adsorption and multi-layer adsorption theories, which was controlled by the widely developed micropores. Specifically, micropore filling adsorption mainly occurred in micropores, including the closed end of slit pores, capillary pores, and ink-shaped pores. Molecular layer adsorption mainly occurred in mesopores and macropores, including the open end of slit pores, plate pores, capillary pores, and ink-shaped pores. Slit pores are mostly intergranular pores, plate pores are mostly interlayer pores (intragranular pores) of clay minerals and microfractures, capillary pores are mostly intergranular pores, and ink-shaped pores are mostly organic matter pores. Besides, the prediction model of CO2 storage quantity in deep shale gas reservoirs of China was established, calculated that 91.5 - 388.89 × 1012 m3 of CO2 could be sealed in adsorbed state in theory, and CO2 was mostly sealed by adsorbed state (higher than 95%) and free state with a good security and low leakage risk.
Keywords
CO2 adsorption,Isothermal adsorption model,CO2 sequestration,Longmaxi shale
Comment submit